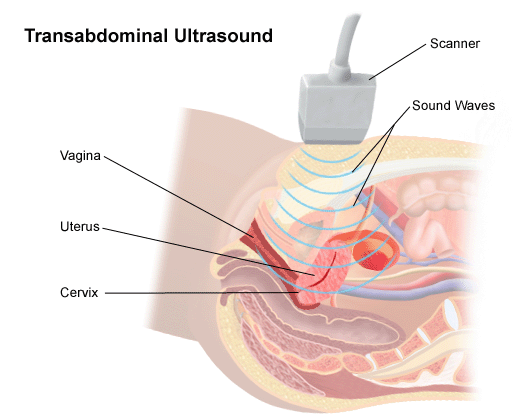
Pelvic Ultrasound/Transabdominal ultrasonography (also called Transabdominal ultrasound imaging or abdominal sonography) is a form of medical ultrasonography (medical application of ultrasound technology) to visualise transabdominal anatomical structures. It uses transmission and reflection of ultrasound waves to visualise internal organs through the abdominal wall (with the help of gel which helps transmission of the sound waves). For this reason, the procedure is also called a transabdominal ultrasound, in contrast with endoscopic ultrasound, the latter combining ultrasound with endoscopy through visualize internal structures from within hollow organs.
Abdominal ultrasound is commonly used in the setting of abdominal pain or an acute abdomen (sudden and/or severe abdominal pain syndrome in which surgical intervention might be necessary), in which it can diagnose appendicitis or cholecystitis.
In cases of infectious mononucleosis splenomegaly is a common symptom and health care providers may consider using abdominal ultrasonography to get insight into a person’s condition. However, because spleen size varies greatly, ultrasonography is not a valid technique for assessing spleen enlargement and should not be used in typical circumstances or to make routine decisions about fitness for playing sports.
